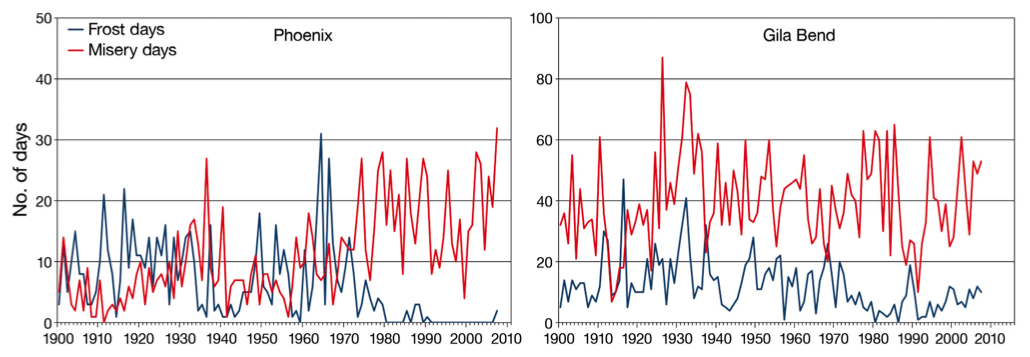
Extreme high temperatures in cities are increasing more rapidly than rural areas, with urban climate dampening the effects of natural climatic fluctuations such as El Niño-Southern Oscillation and Pacific Decadal Oscillation. In a study just published in Climate Research, USC researcher Dr. Darren Ruddell and colleagues showed that maximum temperatures in Phoenix, Arizona showed pronounced increases in recent years, while similar metrics in an undeveloped desert site at Gila Bend showed modest warming. The study illustrates the complex and confounding relationships between well-known short and medium term climate patterns, effects of cities on local climate, and the local effects of global climate change.
Read more about “Historical threshold temperatures for Phoenix (urban) and Gila Bend (desert), central Arizona, USA.”